Issue 21: First sample depot on Mars, Microorganisms can grow Martian bases, water-rich halos on Mars & much more
Missions
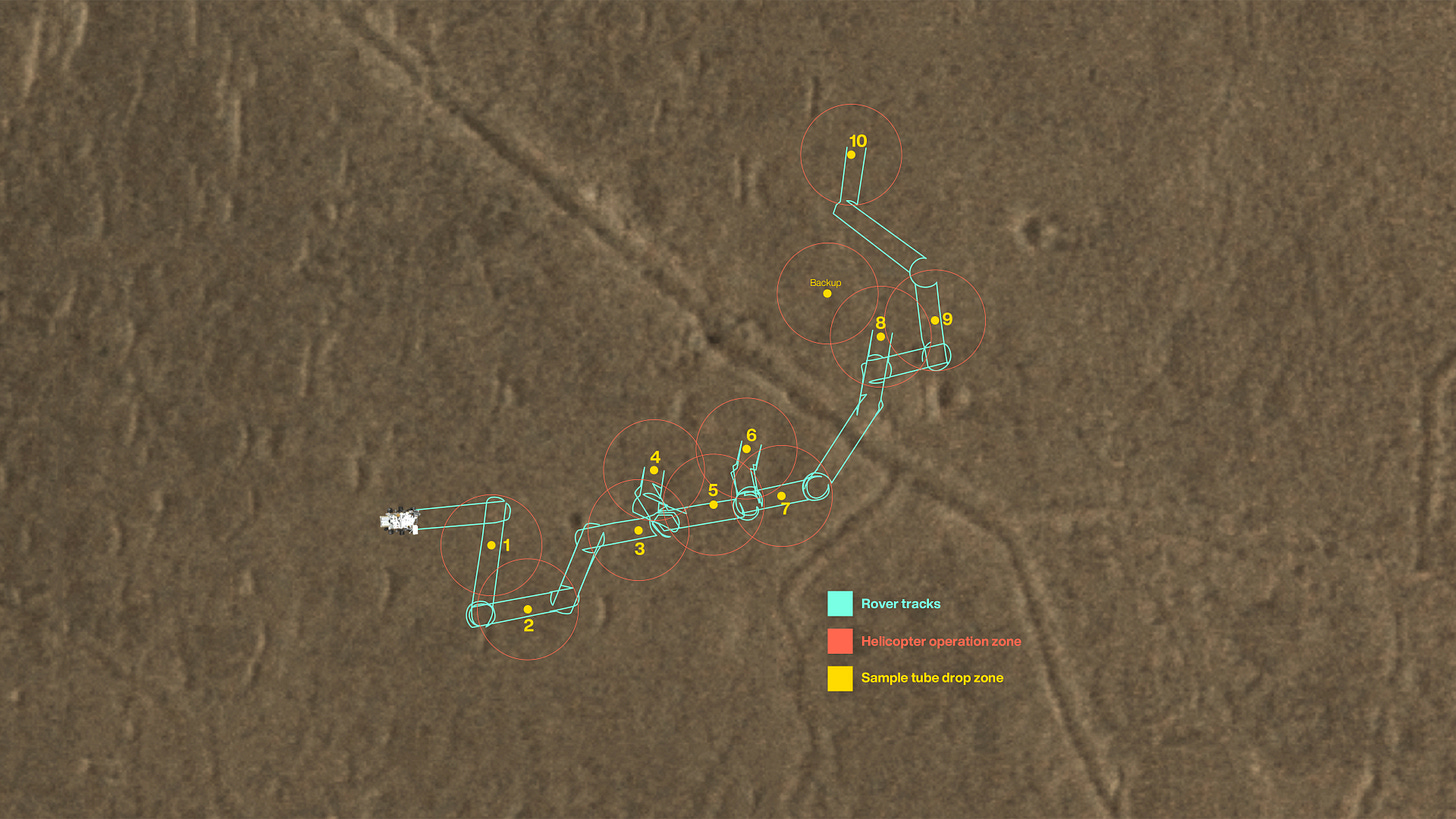
• First sample depot for MSR is ready: On January 24, Mars 2020 rover successfully set up the first sample depot on the red planet. Rover deposited a total of 10 tubes which also includes one atmospheric sample called “witness tube”. This sample will help us verify whether the samples got contaminated by microbes, might have been travelled with the Perseverance rover.
What's next for Percy?: Perseverance is now heading to Rocky Top geologic unit to begin it's third science campaign, Delta Top campaign. The route will take us to the place where once flowing river used to meet the lake! So, we'll mostly get to ‘see' rocks composed of larger grains.
• Ingenuity approaching Perseverance: Since last month, Ingenuity has taken four back-to-back repositioning flights - Flight 40, 41, 42 & 43 - trying to approach Mars 2020 rover.
• “Hey, Zhurong! Can you hear us?” : Since May, China's Mars rover is in 'sleep' mode & was supposed to wake up in late December. But there's no official update even from the core team itself. By luck, if the temperature in area rise above -15°C & once rover will be able to generate more than 140 watts, then the rover will notify us!
Research & Observations
• Cyanobacteria & Fungi can grow building materials on Mars: By utilising In-SITU resources, these two microorganisms can help build Martian bases. This biomineralisation process can be summarised as follows:
Cyanobacteria capture Mars' atmospheric Oxygen & convert it to calcium carbonate.
Calcium carbonate will be used to form biopolymers with the help of synthetic lichen systems.
Martian regolith will be mixed with Biopolymers produced.
Cyanobacteria & Fungi secretes “excellular polymeric substances” which enhance adhesion between regolith particles & biopolymers. This results into strong building materials.
Authors have also detailed process for creating synthetic bacteria & Fungi. And filamentous Fungi can produce large amount of calcium carbonate crystals. But we need to know production rate before anything else.
• Network of water-rich fracture halos on Mars: Recently, Curiosity once again spotted subsurface fracture halos in the Gale crater. And surprisingly, they all are composed of Opal! Opal is a mineraloid which contains silica & water with small amounts of impurities such as Fe. A 1m Halo could house 1-1.5 gallons of water.
As per the new research, these halos seems to be one of the most recent water sources in the history of the Gale crater & can be considered as good reservoirs of water on such dry Mars.
• Martian winds can provide enough power? : Using Mars' global climate models, researchers suggest 50 meter tall wind turbines can produce enough power in the low air pressure environment of the red planet. Since wind speeds vary a lot, these medium-sized turbines would be effective near crater rims or volcano slopes.
Authors have identified some of the most windy places as wind speeds vary with seasons, time, place, etc… But this research is based on models so we can't arrive to a conclusion whether wind can be a stand-alone energy source on Mars or not!
Imagery
Nectaris Fossae and Protva Valles' deformed crust indicates that the region have been lately shaped by tectonics as well as by water!
Recommendation
Take a deeper look at Mars' globe with “Mars Atlas” app! It provides a brief overview of the geology of explored Mars regions & make general public more familiar with the Martian regions!
Want Space to be easily accessible to everyone? So, Assist me to continue publishing all of my writes free for everyone…!









Very Nice Simran. Keep it up..
Nice informative 👍